The initial life of Malala Yousafzai
Malala Yousafzai was born on July 12, 1997, in Mingora, a town in the Swat district of northwestern Pakistan. She was the eldest daughter of Ziauddin Yousafzai, a school owner and education activist, and Tor Pekai Yousafzai, a homemaker. Malala grew up in a family that valued education, and she was encouraged to pursue her studies.
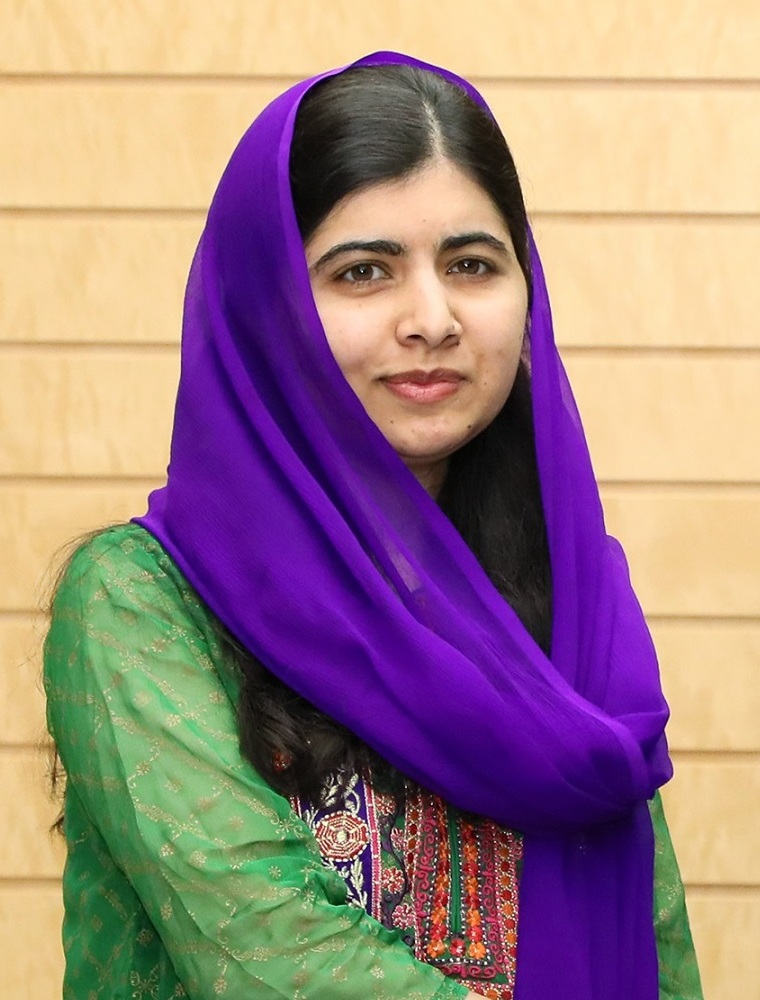

As a child, Malala attended her father’s school, Khushal Public School, and was a top student. She was passionate about learning and was determined to achieve her dreams. She enjoyed reading books, writing, and spending time with her friends.
In 2007, the Taliban began to gain control of the Swat Valley, where Malala lived. The Taliban is a militant group that follows an extremist interpretation of Islam and is known for its brutality, particularly towards women. They imposed strict rules on the people of Swat, including a ban on girls’ education. They destroyed schools and terrorized the local population.
Despite the danger, Malala continued to attend school and speak out for girls’ education. She wrote a blog for the BBC under a pseudonym, Gul Makai, describing life under Taliban rule and advocating for the right to education. Her blog gained international attention, and she became a symbol of hope and resistance.
In 2012, Malala was shot in the head by a Taliban gunman while on her way to school. She was critically injured and had to undergo extensive surgery and rehabilitation. Her attack was widely condemned, and she received an outpouring of support from around the world.
After her recovery, Malala continued to speak out for girls’ education and became a global advocate for human rights. She co-founded the Malala Fund, a non-profit organization that works to empower girls through education. She has spoken at the United Nations, met with world leaders, and received numerous awards for her work, including the Nobel Peace Prize in 2014.
Today, Malala lives in the United Kingdom and continues to advocate for girls’ education and human rights. She is a role model for millions of people around the world and a symbol of hope and courage in the face of adversity.
Education of Malala Yousafzai
Malala Yousafzai’s education began at her father’s school, Khushal Public School, in her hometown of Mingora, in the Swat district of northwestern Pakistan. Malala was an excellent student and was passionate about learning. She enjoyed reading books, writing, and spending time with her friends.
In 2007, when Malala was 10 years old, the Taliban began to gain control of the Swat Valley and imposed a ban on girls’ education. Despite the danger, Malala continued to attend school and speak out for girls’ education. She wrote a blog for the BBC under the pseudonym, Gul Makai, describing life under Taliban rule and advocating for the right to education.

Malala’s activism brought her international attention, and she became a symbol of hope and resistance. However, it also made her a target for the Taliban. In 2012, when Malala was 15 years old, she was shot in the head by a Taliban gunman while on her way to school.
After her recovery, Malala continued to speak out for girls’ education and became a global advocate for human rights. She completed her secondary education in the United Kingdom, where she and her family were granted asylum. She attended Edgbaston High School for Girls in Birmingham and later went on to study at Oxford University, where she completed a degree in Philosophy, Politics, and Economics.
Today, Malala is a prominent advocate for girls’ education and human rights. She co-founded the Malala Fund, a non-profit organization that works to empower girls through education. She has spoken at the United Nations, met with world leaders, and received numerous awards for her work, including the Nobel Peace Prize in 2014. Her story has inspired millions of people around the world to fight for equal access to education and for the rights of women and girls.
Personal life of Malala Yousafzai
Malala Yousafzai is a prominent advocate for girls’ education and human rights, and her personal life has been shaped by her experiences as a young woman fighting for her own education and the rights of others.

Malala was born on July 12, 1997, in Mingora, a town in the Swat district of northwestern Pakistan. She grew up in a family that valued education, and her father, Ziauddin Yousafzai, was a school owner and education activist who instilled in Malala a love of learning and a passion for social justice.
As a child, Malala attended her father’s school, Khushal Public School, and was a top student. She enjoyed reading books, writing, and spending time with her friends. However, her education was disrupted when the Taliban gained control of the Swat Valley in 2007 and imposed a ban on girls’ education. Despite the danger, Malala continued to attend school and speak out for girls’ education, which led to her being targeted by the Taliban and ultimately shot in the head in 2012.
After her recovery, Malala and her family were granted asylum in the United Kingdom, where she completed her secondary education at Edgbaston High School for Girls in Birmingham. She went on to study at Oxford University, where she completed a degree in Philosophy, Politics, and Economics.
Malala’s personal life has also been shaped by her activism and advocacy work. She co-founded the Malala Fund, a non-profit organization that works to empower girls through education, and has traveled around the world to raise awareness about the importance of education and the rights of women and girls.
Despite the global attention and acclaim that she has received for her work, Malala has remained grounded and humble. She has spoken about the importance of staying true to oneself and maintaining a sense of humor in the face of adversity. She has also emphasized the importance of family and community, and the role that they have played in her own life and in the lives of others.
Malala’s personal life has been shaped by her experiences as a young woman fighting for her own education and the rights of others. She has shown incredible resilience, courage, and determination in the face of adversity, and her work has inspired millions around the world to push for greater equality and opportunities for all.
The political career of Malala Yousafzai
Malala Yousafzai is best known for her advocacy work for girls’ education and human rights, and she has not pursued a political career. However, her activism and global profile have put her in contact with political leaders and allowed her to influence policy in significant ways.

Malala has spoken at the United Nations, where she called for worldwide access to education and urged leaders to prioritize the education of girls. She has also met with numerous world leaders, including President Obama, Queen Elizabeth II, and Prime Minister Justin Trudeau of Canada, to discuss education and human rights issues.
In addition to her advocacy work, Malala has also been involved in several initiatives aimed at improving access to education. She co-founded the Malala Fund, a non-profit organization that works to empower girls through education, and has supported initiatives such as the “Girls’ Education Challenge” launched by the UK government.
Despite not being involved in formal politics, Malala has been a powerful force for change and has used her platform to raise awareness about the importance of education and the rights of women and girls. Her work has inspired millions around the world to take action and push for greater equality and opportunities for all.
Noble prize by Malala Yousafzai
Malala Yousafzai was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 2014, along with Indian children’s rights activist Kailash Satyarthi, “for their struggle against the suppression of children and young people and for the right of all children to education.” The Nobel Committee’s decision to award the prize to Malala at the age of 17 was unusual and was seen as a recognition of her exceptional courage and commitment to education and human rights.
Malala’s advocacy work for girls’ education began at a young age. She grew up in the Swat Valley in northwestern Pakistan, where the Taliban had gained control and imposed a ban on girls’ education. Despite the danger, Malala continued to attend school and speak out for girls’ education, which led to her being targeted by the Taliban and shot in the head in 2012.
After her recovery, Malala became a global advocate for education and human rights. She co-founded the Malala Fund, a non-profit organization that works to empower girls through education, and has spoken at the United Nations and met with world leaders to discuss education and human rights issues.
Malala’s Nobel Peace Prize was a recognition of her advocacy work and the impact that she has had on the world. In her Nobel acceptance speech, Malala spoke about the power of education to transform lives and communities. She emphasized the importance of education for all, regardless of gender, race, or social status, and called on leaders around the world to invest in education and create opportunities for young people.
Malala’s Nobel Prize also brought attention to the challenges that many children and young people face in accessing education. She spoke about the need to address issues such as child labor, poverty, and conflict, which can prevent children from attending school and realizing their potential.
The Nobel Prize was a significant milestone in Malala’s journey as an advocate for education and human rights. It brought international attention to her work and helped to amplify her message. However, Malala has also emphasized that the work of promoting education and human rights is ongoing and requires the participation of many individuals and organizations.
Since receiving the Nobel Prize, Malala has continued to speak out for education and human rights. She has visited refugee camps around the world, where she has met with young people who have been displaced by conflict or persecution. She has also continued to advocate for the rights of girls and women, particularly in areas where they face discrimination and violence.
Malala’s Nobel Prize has inspired many people around the world to take action and push for greater equality and opportunities for all. Her story has shown that even in the face of adversity, individuals can make a difference and create positive change in their communities and beyond.
List of books written by Malala Yousafzai
Malala Yousafzai has written several books that tell her story and share her advocacy work for education and human rights. Here is a list of books written by Malala Yousafzai:
- I Am Malala: The Story of the Girl Who Stood Up for Education and Was Shot by the Taliban (2013) This is Malala’s autobiography, co-written with Christina Lamb, which recounts her childhood in Pakistan, her activism for girls’ education, and her recovery after being shot by the Taliban.
- Malala’s Magic Pencil (2017) This is a children’s book written by Malala that tells the story of a young girl who uses her magic pencil to create a better world.
- We Are Displaced: My Journey and Stories from Refugee Girls Around the World (2019) This book, also written by Malala, shares the stories of young women who have been forced to flee their homes due to conflict or persecution.
- Malala: My Story of Standing Up for Girls’ Rights (2018) This is a young readers’ edition of Malala’s autobiography, which is adapted for a younger audience.
- The Girl Who Stood Up for Education and Changed the World (2012) This is a picture book written by Malala, aimed at younger children, that tells the story of her activism for girls’ education.
In addition to these books, Malala has also written numerous articles and given speeches around the world on issues related to education and human rights.
Five important facts about Malala Yousafzai
Here are five important facts about Malala Yousafzai:
- Malala was born on July 12, 1997, in Mingora, Pakistan. She grew up in the Swat Valley region of Pakistan and attended a school that her father had founded.
- Malala became an advocate for girls’ education at a young age and began writing a blog for the BBC under a pseudonym when she was just 11 years old. Her blog chronicled life under Taliban rule in the Swat Valley and advocated for girls’ right to education.
- In 2012, Malala was shot in the head by a Taliban gunman while she was on her way to school. She was targeted for her outspoken advocacy for girls’ education. She survived the attack and has since become a global advocate for education and human rights.
- In 2014, Malala was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize, becoming the youngest ever Nobel laureate. She shared the prize with Indian children’s rights activist Kailash Satyarthi “for their struggle against the suppression of children and young people and for the right of all children to education.”
- Malala is the co-founder of the Malala Fund, a non-profit organization that works to empower girls through education. The Malala Fund has invested in education programs in countries such as Pakistan, Nigeria, and Syria and has worked to raise awareness about the importance of education for girls around the world.
How Malala Yousafzai is an inspirational character in the 21st century
Malala Yousafzai is an inspirational character in the 21st century for several reasons:
- Her advocacy for education: Malala’s advocacy for education, particularly for girls, has inspired millions around the world. Her courage and determination in the face of opposition from the Taliban and other extremists have made her a symbol of the struggle for girls’ education globally.
- Her resilience: Despite being shot in the head by a Taliban gunman at a young age, Malala did not let this setback deter her from her activism. She has continued to speak out and work for education and human rights and has become a leading voice on these issues.
- Her message of peace: Malala has consistently advocated for peaceful solutions to conflicts and has emphasized the importance of education in promoting understanding and tolerance. Her message of peace and non-violence has resonated with people around the world.
- Her leadership: Malala’s leadership in the fight for education and human rights has inspired others to take action and has brought attention to these issues on a global scale. She has shown that one person can make a difference and that young people can be powerful agents of change.
- Her impact: Malala’s work has had a significant impact on the world. She has raised awareness about the importance of education for girls and has inspired governments and organizations to invest in education programs for girls around the world. Her advocacy has also helped to change attitudes towards girls’ education and has encouraged more girls to pursue their dreams and reach their full potential.
What are the top 3 ways in which Malala has changed the world?
Malala Yousafzai has had a significant impact on the world and has brought attention to issues related to education and human rights. Here are three of the top ways in which Malala has changed the world:
- Advocating for girls’ education: Malala’s advocacy for girls’ education has brought attention to the barriers that many girls face in accessing education, particularly in developing countries. Her work has inspired governments and organizations to invest in education programs for girls, and has helped to change attitudes towards girls’ education globally.
- Promoting peace and non-violence: Malala has consistently advocated for peaceful solutions to conflicts and has emphasized the importance of education in promoting understanding and tolerance. Her message of peace and non-violence has resonated with people around the world, and she has become a leading voice on issues related to conflict resolution and human rights.
- Empowering young people: Malala’s work has empowered young people, particularly girls, to speak out and take action on issues that matter to them. She has shown that young people can be powerful agents of change, and has encouraged young people to take an active role in shaping their communities and the world around them. Through the Malala Fund, she has supported education programs and initiatives that empower girls and young people to realize their full potential.
What was the main message of Malala?
The main message of Malala Yousafzai is the importance of education and the empowerment of girls and women. She has dedicated her life to advocating for access to education, particularly for girls in developing countries, and has become a leading voice on issues related to education, human rights, and gender equality. Her message is one of hope, resilience, and empowerment, and has inspired millions around the world to take action and work toward a more just and equitable society.
Malala’s journey began when she was just a young girl living in the Swat Valley in Pakistan. She grew up in a society where girls were often denied access to education, and where extremist groups like the Taliban were gaining power and imposing their will on the population. Despite these challenges, Malala was determined to get an education and to help other girls do the same. She began speaking out publicly about the importance of education for girls, and her advocacy work quickly caught the attention of the international community.
In 2012, when Malala was just 15 years old, she was targeted by the Taliban for her activism. She was shot in the head by a Taliban gunman while on her way to school, and she was critically injured. Miraculously, she survived the attack and went on to receive medical treatment in the United Kingdom. While recovering, she continued to speak out about the importance of education, and her message of hope and resilience resonated with people around the world.
Malala’s message is one of the transformative power of education. She believes that education is the key to breaking the cycle of poverty, promoting economic development, and achieving gender equality. She has emphasized that education is not only a fundamental right, but also a powerful tool for social change. By educating girls, she believes that we can build more just and equitable societies, where everyone has the opportunity to reach their full potential.
Malala has also emphasized the importance of gender equality and women’s empowerment. She believes that girls and women have the right to be treated with dignity and respect, and that they should have the same opportunities as boys and men to pursue their dreams and reach their full potential. She has called on governments and organizations to invest in education and other programs that support the empowerment of girls and women, and has become a leading advocate for women’s rights globally.
Another important aspect of Malala’s message is her emphasis on peace and non-violence. She has consistently advocated for peaceful solutions to conflicts, and has emphasized the importance of education in promoting understanding and tolerance. She believes that we must work towards a world where all individuals have the opportunity to live in peace and dignity, and has called on people to reject violence and extremism in all its forms.
Malala’s message is one of hope and empowerment and has inspired millions around the world to take action and work towards a more just and equitable society. She has shown that one person can make a difference and that young people can be powerful agents of change. Through her advocacy work, she has brought attention to important issues related to education, human rights, and gender equality, and has inspired others to join her in the fight for a better world. Overall, Malala’s message is one of resilience, courage, and hope, and has left a lasting impact on the world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Malala Yousafzai is a remarkable young woman whose life and work have inspired millions around the world. She has dedicated her life to advocating for the importance of education and the empowerment of girls and women and has become a leading voice on issues related to human rights, gender equality, and peace.
Malala’s journey began when she was just a young girl growing up in the Swat Valley in Pakistan, where she faced significant challenges in accessing education due to gender discrimination and extremism. Despite these obstacles, Malala remained committed to her education and began speaking out publicly about the importance of education for girls. Her advocacy work quickly gained attention, and she became a powerful voice for change.
In 2012, Malala was targeted by the Taliban for her activism and was shot in the head while on her way to school. Miraculously, she survived the attack and went on to receive medical treatment in the United Kingdom. While recovering, she continued to speak out about the importance of education, and her message of hope and resilience resonated with people around the world.
Since then, Malala has become a global icon and a leading advocate for education and women’s rights. She has received numerous awards and honors for her work, including the Nobel Peace Prize, and has inspired millions around the world to take action and work toward a more just and equitable society.
Overall, Malala’s life and work serve as an inspiration to us all. She has shown us the transformative power of education and the importance of standing up for what we believe in, even in the face of adversity. Her message is one of hope, resilience, and empowerment, and has left a lasting impact on the world.